

Two (or more) resistors with their heads directly connected together and their tails directly connected together are in parallel, and they can be reduced to one resistor using the equivalent resistance equation for resistors in parallel.General rules for doing the reduction process include:

The current flowing through each resistor can then be found by undoing the reduction process. This allows the current to be determined easily. Generally, the total resistance in a circuit like this is found by reducing the different series and parallel combinations step-by-step to end up with a single equivalent resistance for the circuit. Many circuits have a combination of series and parallel resistors. Flipping this upside down gives 18/6 = 3 ohms, which is certainly between 2 and 6.Ĭircuits with series and parallel components The smallest resistance is 6 ohms, so the equivalent resistance must be between 2 ohms and 6 ohms (2 = 6 /3, where 3 is the number of resistors).ĭoing the calculation gives 1/6 + 1/12 + 1/18 = 6/18. You have three resistors in parallel, with values 6 ohms, 9 ohms, and 18 ohms. The equivalent resistance will always be between the smallest resistance divided by the number of resistors, and the smallest resistance. If you have two or more resistors in parallel, look for the one with the smallest resistance. When calculating the equivalent resistance of a set of parallel resistors, people often forget to flip the 1/R upside down, putting 1/5 of an ohm instead of 5 ohms, for instance. So, two 40-ohm resistors in parallel are equivalent to one 20-ohm resistor five 50-ohm resistors in parallel are equivalent to one 10-ohm resistor, etc. In this case the equivalent resistance of N identical resistors is the resistance of one resistor divided by N, the number of resistors. If the resistors in parallel are identical, it can be very easy to work out the equivalent resistance. Note that the currents add together to 5A, the total current. The voltage across each resistor is 10 V, so: The individual currents can also be found using I = V / R. If the values of the three resistors are: In this case the current supplied by the battery splits up, and the amount going through each resistor depends on the resistance. The total resistance of a set of resistors in parallel is found by adding up the reciprocals of the resistance values, and then taking the reciprocal of the total:Įquivalent resistance of resistors in parallel: 1 / R = 1 / R 1 + 1 / R 2 + 1 / R 3 +.Ī parallel circuit is shown in the diagram above. The voltage across each resistor in parallel is the same. The current in a parallel circuit breaks up, with some flowing along each parallel branch and re-combining when the branches meet again. The current through each resistor would be 0.5 A.Ī parallel circuit is a circuit in which the resistors are arranged with their heads connected together, and their tails connected together. With a 10 V battery, by V = I R the total current in the circuit is: The current flows through each resistor in turn.
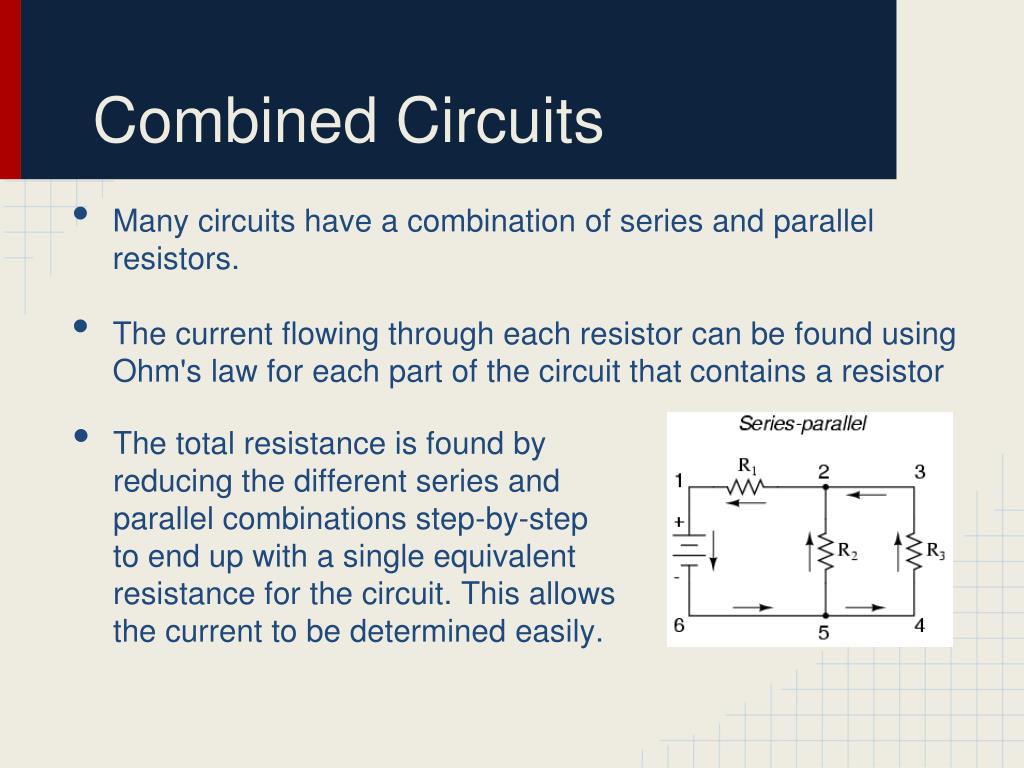
Ī series circuit is shown in the diagram above. The total resistance of the circuit is found by simply adding up the resistance values of the individual resistors:Įquivalent resistance of resistors in series : R = R 1 + R 2 + R 3 +. The current is the same through each resistor. Series and Parallel Circuits Series and Parallel CircuitsĪ series circuit is a circuit in which resistors are arranged in a chain, so the current has only one path to take.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
